Ecodesign level of the website

- Ecoindex score : 77,59/100
- Average water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 21.74 (equal to 2 cases of mineral water).*
- Average greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.45 (equal to an 8 km journey in a combustion-engine car).*
Assessment method
Like all digital productions, this website has an environmental impact, details of which are provided on this page using standard metrics.
We use the
EcoIndex reference framework developed by
GreenIT.fr to assess the website’s environmental performance. This is quantified on the basis of two kinds of metrics:
- Ecodesign level of the website. This metric assesses the implementation of best practices to reduce a web page’s impact. The level achieved is represented by a rating from A to G (A being the best) along with an absolute score of 0 to 100 (100 being the best).
- Water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions relating to page loading. This metric shows fresh water consumption (cl) and greenhouse gas emissions (g CO2e) relating to loading a web page.
For summary purposes, four types of data are used:
- Ecodesign level for the website’s 5 most visited pages
- Ecodesign level for 5 typical user scenarios for the website
- Water consumption (in litres) and greenhouse gas emissions (kg CO2e) relating to loading a web page for 1 user, per 1,000 users.
- Water consumption (in litres) and greenhouse gas emissions (kg CO2e) relating to executing a scenario for 1 user, per 1,000 users.
The analysis was done on 20 May 2022 and may be subject to change: the environmental impact as quantified below represents a snapshot at a given time.
Ecodesign level of the website’s 5 most visited pages

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 23.2 (equal to 3 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.55 (equal to a 9 km journey in a combustion-engine car).

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 21.7 (equal to 2 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.44(equal to an 8 km journey in a combustion-engine car).

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 22 (equal to 3 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.46 (equal to a 9 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
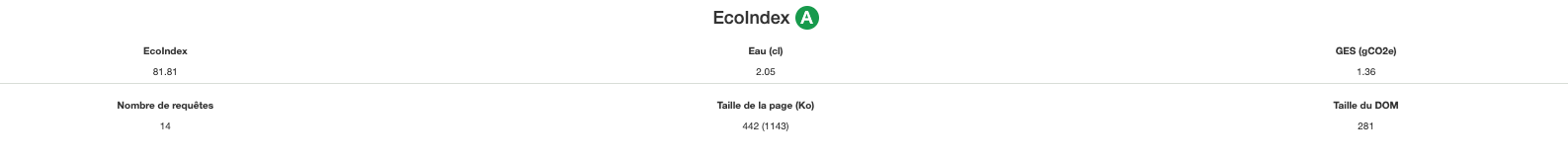
- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 20.6 (equal to 2 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.37 (equal to an 8 km journey in a combustion-engine car).

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 21.2 (equal to 2 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 1.41 (equal to an 8 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Impact for 5 user scenarios on the website
Scenario 1: Contact Covéa Affinity about one of its solutions
- Objective: To request information about one or more solutions
- Target clickstream: load home page, view solutions on offer, contact to request information
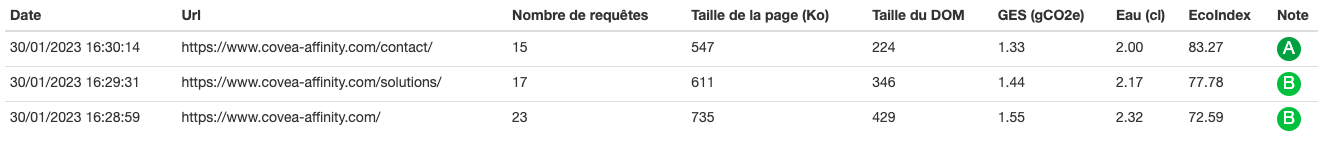
- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 64.9 (equal to 7 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 4.32 (equal to a 24 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Scenario 2: Contact Covéa Affinity to get a tailor-made quotation
- Objective: To make a personalised request
- Target clickstream: load home page, click on “Find out more” call to action and arrive on the corresponding page, click on call to action to contact Covéa Affinity.
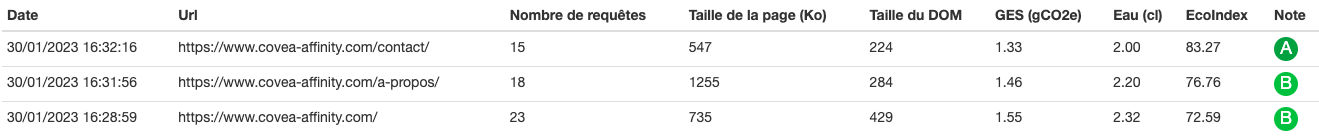
- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 65.2 (equal to 7 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 4.34 (equal to a 24 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Scenario 3: View commitments
- Objective: access commitments from the “About” page
- Target clickstream: load “About” page, click on “Our commitments” call to action and arrive on the corresponding page.

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 43.2 (equal to 5 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 2.87 (equal to a 16 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Scenario 4: Access the “Our commitments” page
- Objective: access commitments from the home page
- Target clickstream: load “About” page, click on “Our commitments” call to action and arrive on the corresponding page.

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 44.4 (equal to 5 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 2.96 (equal to a 17 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Scenario 5: View partners
- Objective: access to partners
- Target clickstream: load home page, click on “Who are we”

- Water consumption per 1,000 users (in litres): 43.8 (equal to 5 cases of mineral water).
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1,000 users (in kg of CO2e): 2.92 (equal to a 16 km journey in a combustion-engine car).
Ecodesign
Ecodesign uses a methodology and best practices to reduce the website’s impact on the environment. In concrete, this will be achieved by limiting the technical resources required to display a page or execute a functionality, while still meeting the user’s needs as best possible.
Are you a digital professional and do you want to reduce the environmental impact of your websites? Here are a few best practices to adopt:
A few ergonomics and design best practices
- Limit the number of functionalities at the design stage
- Get rid of unused functionalities
- Limit the number of carousels
- Choose lightweight fonts
- Opt for simple, pared-back designs
- Adopt a “mobile-first” approach where possible
- Opt for infinite scrolling pagination
- Avoid automatic reading and downloading of videos and sounds
- Optimise the user experience
- ...
A few content management best practices
- Give preference to images over videos
- Limit the number of images on each page
- Optimise the size of images in the target format
- Compress images using a tool like TinyPNG
- Compress PDFs using a tool like iLovePDF
- Limit use of animated GIFs
- Give preference to glyphs over images
- ...
A few development best practices
- Offer asynchronous processing where possible
- Only use the essential parts of JS and CSS libraries
- Cache frequently used data
- Limit the number of HTTP API calls
- Reduce the volume of stored data to what is strictly necessary
- Use the latest language version
- Provide a textual alternative to multimedia content
- Separate CSS
- Don’t change the DOM when using it
- Use lazy loading
- Validate pages with W3C
- Add Expires or Cache-Control headers
- Compress text files: CSS, JS, HTML and SVG
- Create an efficient sitemap
- ...
A few hosting best practices
- Choose an environmentally responsible hosting company
- Install the minimum required on the server
- Make use of managed services
- Ensure that servers run at optimum energy efficiency
- Reduce server logs to what is necessary
- Apache Vhost: disable AllowOverride
- Use virtualised servers
- Use an asynchronous server
- Store data in the cloud
- ...
To create your environmental statement:
→ Access documentation
To view the full list of web ecodesign best practices:
→ Access the GreenIT website
→ Access the GreenIT depository (GitHub)
For more information about EcoIndex:
Find out more about the EcoIndex reference framework
Access the EcoIndex website
*Average environmental impact of this website’s 5 most visited pages.











